Alzheimers
Stem Cell Therapy is seen as a strong candidate to treat Alzheimer’s and is currently undergoing human clinical trails to determine it’s efficacy in slowing or reversing the symptoms.
Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the brains and is the most common cause of dementia, affecting memory, thinking and behavior.
Current Treatment
No known cure for Alzheimer’s and patients are currently treated with drugs that help to reduce the symptoms such as improving memory, or helping with daily tasks
Stem Cell Update
Researchers at University of Miami plans clinical trials to study the use of stem cells to slow or reverse the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. more….
What Is Alzheimer’s?
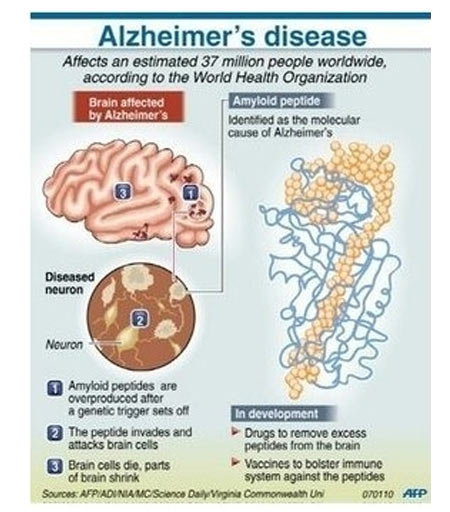 Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the brains and is the most common cause of dementia, affecting memory, thinking and behavior. It is estimated that there are 46.8 Million people worldwide who are suffering from dementia and is expected to reach a worldwide figure of 131.5 Million people by 2050. This has alarmed governments worldwide and it would greatly increase the cost of healthcare and affect the socioeconomic levels of the country.
Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease that affects the brains and is the most common cause of dementia, affecting memory, thinking and behavior. It is estimated that there are 46.8 Million people worldwide who are suffering from dementia and is expected to reach a worldwide figure of 131.5 Million people by 2050. This has alarmed governments worldwide and it would greatly increase the cost of healthcare and affect the socioeconomic levels of the country.
Researchers still do not know the exact cause of Alzheimer’s but believe multiple factors including genetic makeup, lifestyle and environmental factors contribute to the development of this debilitating disease. Although root cause is unknown, research has highlighted that people affected with this disease have displayed an abnormal build up of certain proteins in the brain. One of these proteins, known as amyloid beta, group together, forming “plaques” while another protein called tau gets twisted together and form “tangles”. It is believed that these proteins prevents neurons in the brains from communicating properly or even prevent them from getting the nutrients it needs, causing these neurons to die off and loss a larger amount as the disease progresses.
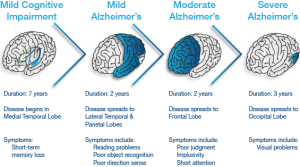
People suffering from Alzheimer’s usually show milder form of symptoms in the beginning such as forgetfulness, and gets worse over time, eventually affecting ability to do daily tasks. Some of the symptoms usually exhibited are:
- Memory loss
- Difficulty completing normal tasks
- Difficulty with interpretation of visual information
- Reduced Judgment
- Inability to speak or write
- Change Mood
Current Treatment Methods for Alzheimer’s
There are currently no known cure for Alzheimer’s and patients are currently treated with drugs that help to reduce the symptoms such as improving memory, or helping with daily tasks. The class of drugs known as cholinesterase inhibitors (aricept, Exelon, Razadyne) are used during early to moderate stages of Alzheimer whilst memantine (Namenda) is used from moderate to severe stage of alzheimer’s sometimes together with aricept as well.
Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s
Stem cell treatment for Alzheimer’s is currently in the early stage and as the brain has many different types of neurons in all parts of the brain, it poses a complex disease to treat. However some stem cell therapies are beginning to enter clinical trials, according to scientists who are involved in a recent symposium titled “Accelerating The Cure For Alzheimer’s Disease To Regenerative Medicine.”
Many forms of research are ongoing and are generally focused in the following areas:
There are many ongoing efforts to understand how stem cell therapy is able to help people with Alzheimer’s. One of the main centres is the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine, where you can view the areas of research being conducted specifically to understand Alzheimer’s.
FOR MORE INFORMATION:
CONSULT US!
Unsure whether this treatment is right for you? Book your consultation with us ONLINE now!
